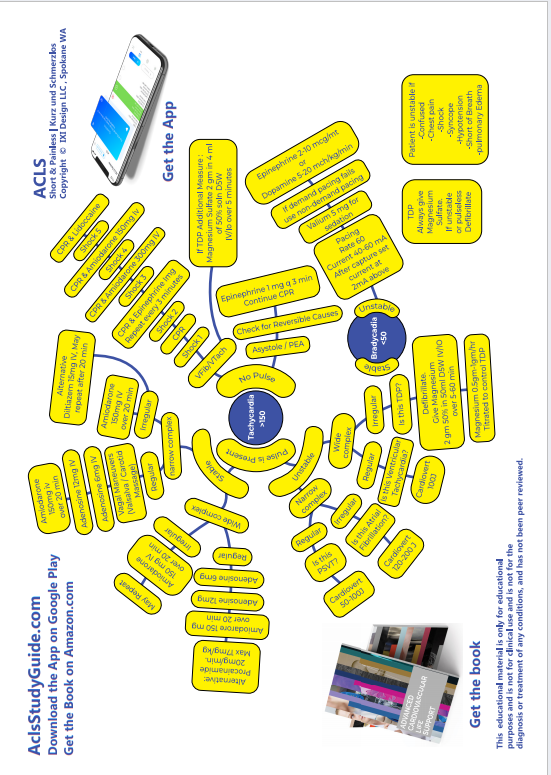
POST RESUSCITATION CARE
- Oxygenation : Maintain SpO2 >94%
- Perfusion: Capnography can be used as a guide. Target PETCO2 35-40mm Hg
-
BP maintenance:
- 1-2 L Normal Saline or Ringer Lactate. Do not give hypotonic fluids
- SBP must be kept >90, and MBP > 65
- Dopamine 2-10 microgram / kg /minute
- Norepinephrine 0.1-0.5 micrograms/kg/minute
- Epinephrine 0.1-0.5 micrograms /kg/ minute
-
Hypothermia: Maintain 32-34 degree C
- Use bladder or esophageal thermometers
-
12 Lead EKG
- The reason the most common cause of arrest is MI
- Look for new ST elevation or new LBBB, assess QTc
- Concurrent PCI and hypothermia are safe
- Coma is not a contraindication to cardiac intervention
- If STEMI noted , or if there is a high index of suspicion for AMI, take to cath suite.
-
Continuous cardiac monitoring
- Treat arrhythmias as they happen instead of prophylaxis
-
Echocardiogram to look for myocardial stunning
- May need Dobutamine 5-10 micrograms /kg/minute
- Remove reversible causes
-
Endovascular or surface cooling 32 degrees to 34 degrees C for 24h.
- After 24 h slow rewarming at 0.25 deg C per hour
- Neuro: serial neuro checks
- EEG monitoring if comatose
- Watch for hypokalemia and correct if needed
- Monitor urine output, maintain euvolemia
- Treat hypoglycemia if <80mg/dl
- Treat Hyperglycemia if >180mg/dl
Read Other Topics
Read All Pages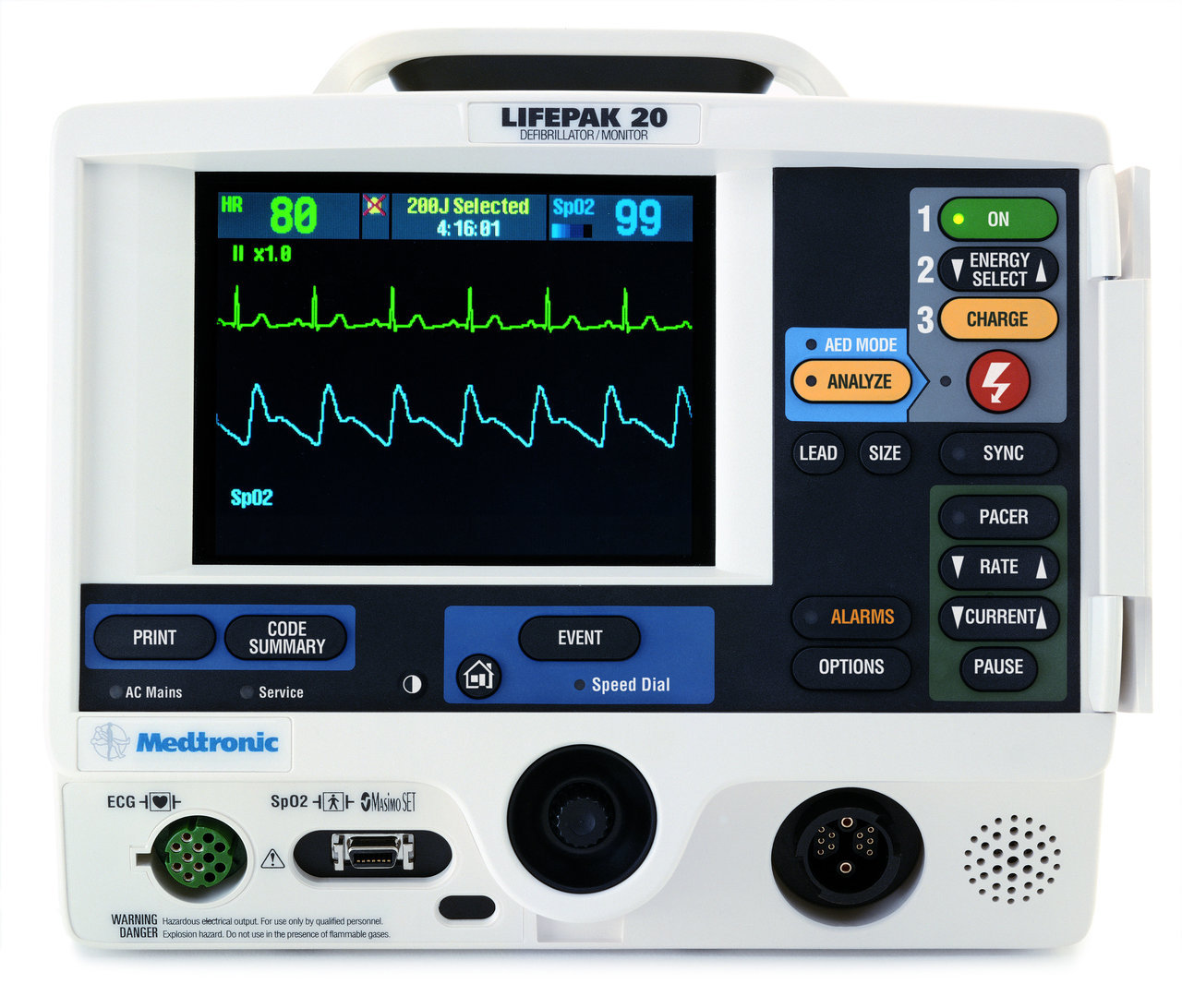
Ventricular Fibrillation
It this was an unwitnessed arrest, meaning it did not happen in front of you, you should give him 5 cycles of CPR...
Read More
Infant Cpr
Perform 30 chest compressions. Use two fingers and deliver the compressions over the breastbone, just below the nipple line...
Read More