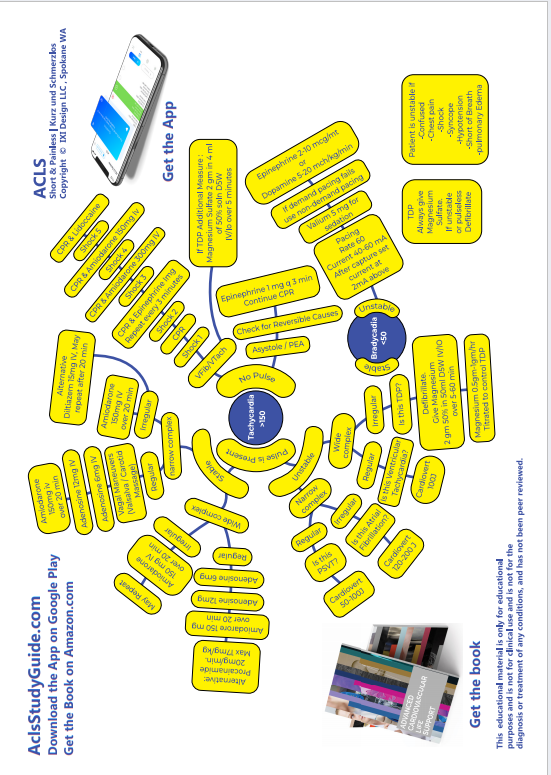
ASYSTOLE
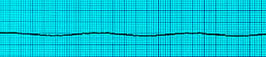
Asystole
Confirm the presence of Asystole on two separate leads , because fine ventricular fibrillation can mimic asystole.
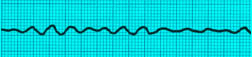
Fine Ventricular Fibrillation
The first and most important thing to remember about Asystole is : DO NOT SHOCK ASYSTOLE.
Now repeat after me: "I will not shock asystole. I will not shock asystole. I will not shock asystole. " And if you do, you will flunk your test :-)
What you do instead is, CPR ! Just good old CPR, and lots of it:
5 Cycles of CPR: 30 chest compressions -> head tilt chin lift to open airway -> 2 breaths
After every 5 cycles of CPR, check the rhythm. If he is still in Asystole, continue CPR.
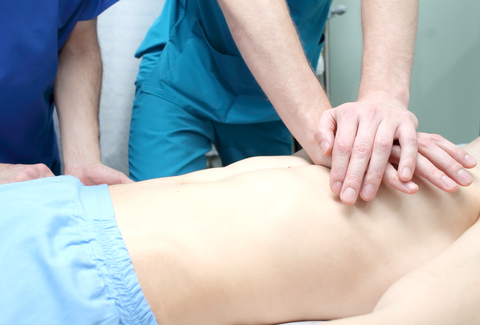
30 Chest Compressions | 100-120/minute rate | 2-2.4 inch depth
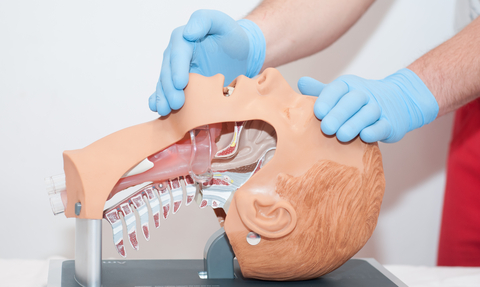
Head Tilt Chin Lift to open the Airway

Two Breaths
There is other things that the rest of the team should be doing during CPR:
- Start an IV line
- Draw and send off venous and arterial blood
- Interrupt CPR for 10 seconds at some point to insert an Endotracheal tube. Remember, 10 seconds means 10 seconds and no more. Once an ET tube is in place, chest compressions can continue nonstop at 100-120 per minute without pausing for breaths. Breaths should be given every 6-8 seconds. Remember, once you put an ET tube in, confirm position by ausculation and capnography. If you dont know how to put an ET tube in, use a Combitube, insert blindly; use the blue cuff to ventillate while listening for air entry in both lungs. If you instead hear epigastric sounds, stop using the blue tube to ventillate, use the other lumen instead to ventillate.
- IV fluids running full
- Check for and correct any potential causative factors, namely hypovolemia, hypoxia, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, hyperkalemia, hydrogen ion imbalance (acidosis), toxins, cardiac tamponade, tension pneumothorax, thrombosis coronary or pulmonary.
Medications to be Given:
- While CPR is going on, give Epinephrine 1 milligram IV, every 3 minutes.
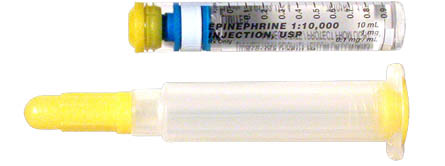
Now, about the role of pacing in asystole:
IF IT WAS A WITNESSED ARREST, AND YOU ARE RIGHT THERE , AND TCP IS AVAILABLE, AND THE PATIENT IS IN ASYSTOLE, TCP SHOULD BE ATTEMPTED IMMEDIATELY.
Exam findings can give us a clue to the etiology of asystole:
- If there is Jugular venous distension, consider cardiac tamponade, pulmonary embolism and pneumothorax.
- If there is tracheal deviation consider pneumothorax. If air entry is diminished on one side of the chest consider pneumothorax.
- If there is a history of suicide attempts, consider drug toxicity.
- Treat beta-blocker or calcium channel overdose with glucagon 1mg iv and calcium chloride 10% 10mg/kg IV.
- Treat narcotic overdose with naloxone 2mg iv. Treat tricyclic overdose with sodium bicarb 1meq/kg IV.
- Treat hyperkalemia also with sodium bicarbonate 1 meq /kg IV.
If the patient remains in asystole for 10 minutes, it is time to call off the code. You did your best and that is all you can do.
Read Other Topics
Read All Pages
Ventricular Fibrillation
It this was an unwitnessed arrest, meaning it did not happen in front of you, you should give him 5 cycles of CPR...
Read More
Infant Cpr
Perform 30 chest compressions. Use two fingers and deliver the compressions over the breastbone, just below the nipple line...
Read More