Knowledge Base
Quantitative Waveform Capnography (ETCO2 monitoring)
Normal ETCO2 is 35-40mm
No reading means the ET is in the esophagus.
Effective CPR will keep ETCO2 >=10
If it is >35mm predicts ROSC
EKG
RATE
Rate= 1500 / number of small squares between two R waves
OR
Rate = 300/number of large squares between two R waves
If the patient is tachycardia, the technique is to count the number of large boxes between one R wave and the R wave after the next. (300 / the number of boxes). Now multiply this by 2 and you have the rate.
RHYTHM
Rhythm: regular or irregular
Follow the R waves to help determine this. Be careful not to mistake PACs and PVCs as 'irregular rhythm'.
P WAVES
Atrial activity: P waves : are they present, are they regular, do they look the same, how are the related to QRS (is there one P before each QRS, and if so is the PR interval the same)
Sinus Rhythm: P wave is upright in lead II and there should be a P before each QRS. If P is negative in II, it is not sinus rhythm. Rate 60-99
Sinus Bradycardia: Sinus Rhythm with Rate <60
Sinus Tachycardia: Sinus Rhythm with Rate >100
If the rate >=150 it is no longer SINUS Tachycardia. It tachycardia, and based on the whether the complexes are wide (ventricular) or narrow (supraventricular) they are further identified.
Sinus Arrhythmia: Sinus Rhythm, PR fixed but RR intervals vary. If the rhythm is irregular but the PR is fixed and the Ps are intact,the issue is at the level of the sinus node.
PR INTERVAL
Normal PR interval is 3-5 small boxes (0.12 - 0.2sec)
QRS
QRS: narrow or wide (>=3 small boxes)
Upper limit of QRS duration: 0.1 sec (occupies two and half small boxes)
One small box is 0.04 sec
If QRS is occupying 3 small boxes, it is wide complex.
Junctional Rhythm : Range is 40-60. A junctional rhythm that is faster than this is called accelerated junctional rhythm. (Think Digitalis toxicity)
Ventricular Rhythm: Range is 20-40.
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
Check ventricular rate. If 70-100, it is Atrial Fibrillation with Controlled Ventricular Response. >100 is AF with Rapid Ventricular Response.
ATRIAL FLUTTER
Atrial Rate around 250-300/mt
Ventricular rate will be half of this or 1/4 of this.
ECTOPIC BEATS
PACs (a P-QRS that is occuring too early)
PVC (a ventricular beat that is occuring too early)
Two PVCs in a row: Couplet
Three PVCs in a row: Ventricular Tachycardia, unsustained.
If VT lasts >=20 seconds it is Sustained VT.
(A standard EKG strip is 6 seconds long!)
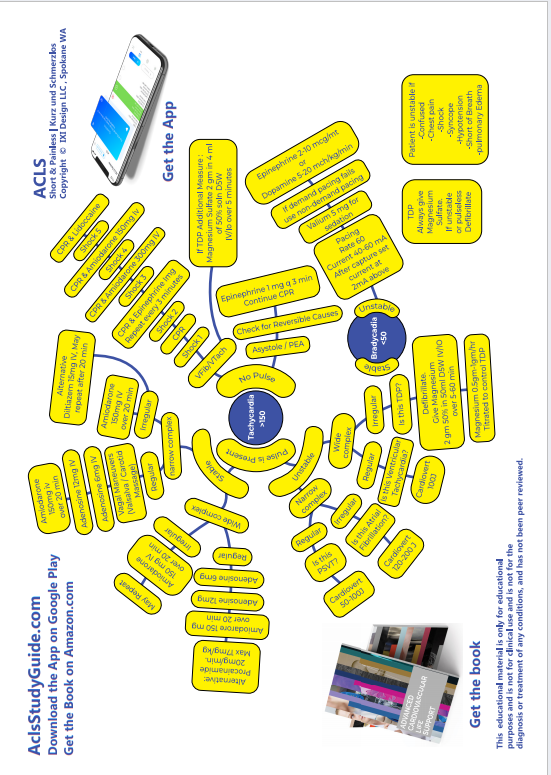
TACHYCARDIA
If no pulse: Defibrillate
If patient is unstable: Cardiovert
BRADYCARDIA
If patient is unstable: TCP (Transcutaneous Pacing)
Read Other Topics
Read All Pages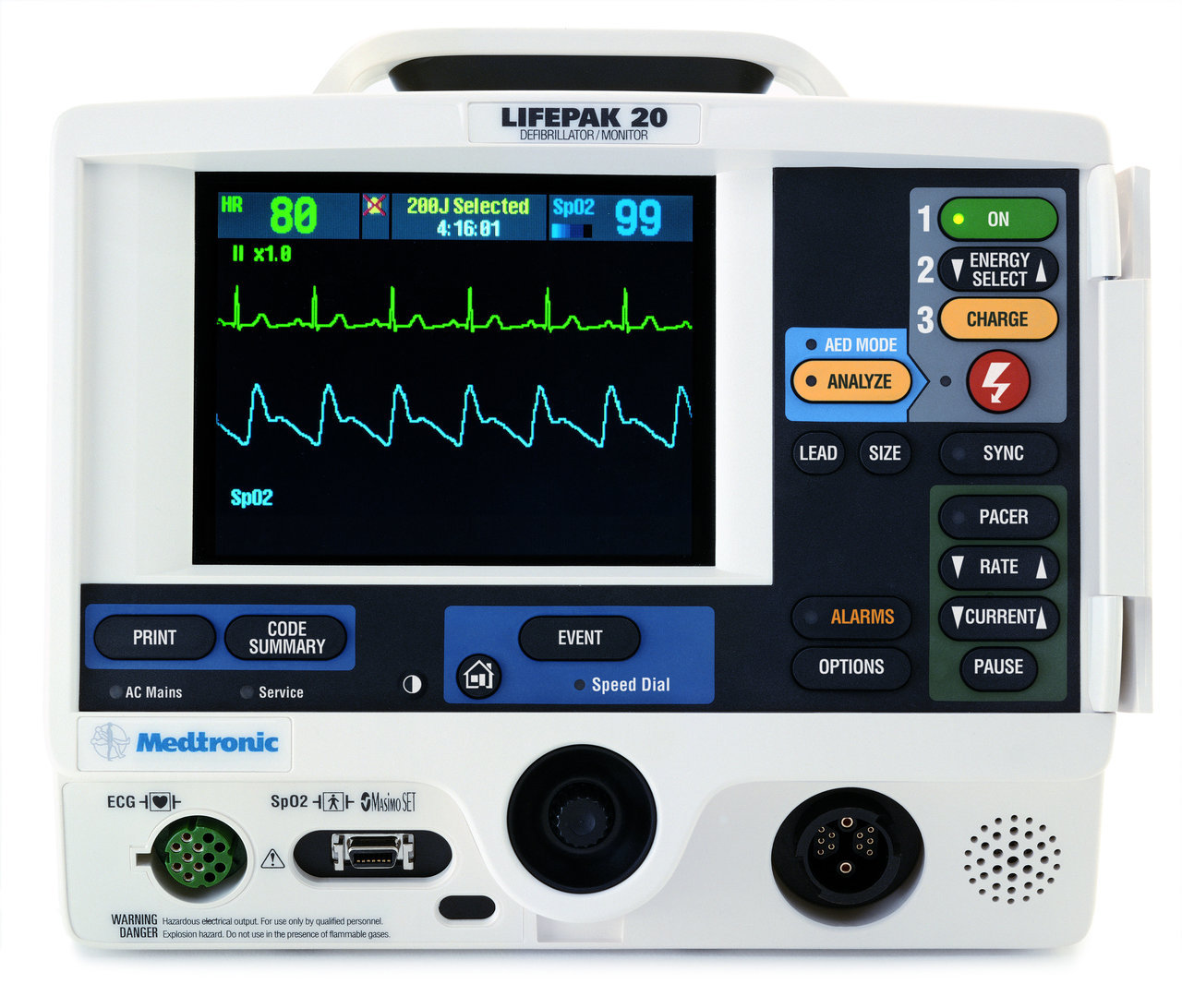
Ventricular Fibrillation
It this was an unwitnessed arrest, meaning it did not happen in front of you, you should give him 5 cycles of CPR...
Read More
Infant Cpr
Perform 30 chest compressions. Use two fingers and deliver the compressions over the breastbone, just below the nipple line...
Read More