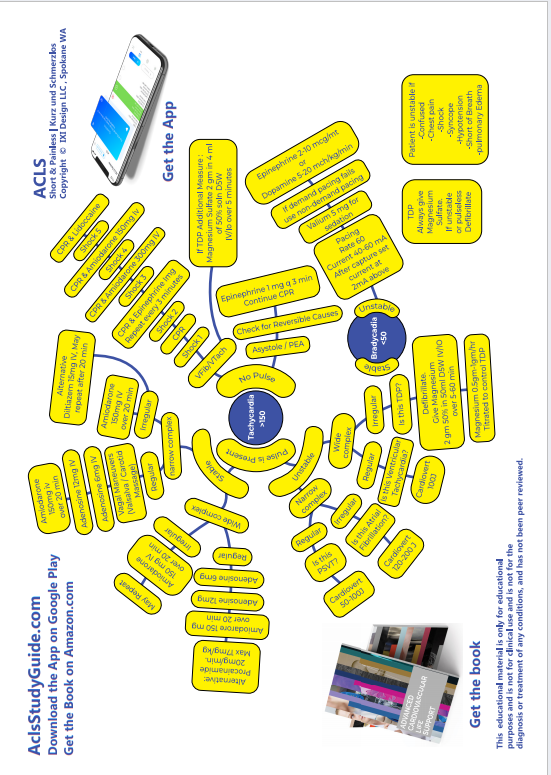
CHEST PAIN
CHEST PAIN (EMS RESPONSE)
- Activate Cath Lab
- Aspirin 325mg Oxygen
- Oxygen
- 12 Lead EKG
- Manage Pain
ER (IMMEDIATE STEPS)
- Oxygen
- Aspirin
- Nitroglycerin
- Morphine
- 12 lead EKG
- CxR
- IV access, physical exam, vitals
ST ELEVATION MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION STEMI
Does the patient have chest pain?
- Is the duration < 12 hours (sometimes 12- 24 hour duration may also qualify)
Is there evidence of ST ELEVATION Myocardial Infarction?
- >1mm ST elevation in two contiguous leads
STEMI EKG definition : new ST elevation at the J point in 2 contiguous leads of 2mm or more in men or 1.5 mm in women in leads V2-V3 and/or 1 mm or more in other contiguous limb leads. (1mm= 0.1 mV)
STEMI equivalents :
- Posterior wall MI : ST depression in 2 or more precordial leads (V1-V4).
- Left main coronary artery occlusion, ST depression in at least 6 leads with coexistent ST elevation in lead aVR.
- New Left Bundle Branch Block
Our objective is :
- If patient can be taken to PCI and procedure started with in 90 minutes this would be ideal
- The next option is Fibrinolysis (Alteplase) which should be started within 30 minutes.
Meanwhile start Adjuvant therapies (Do NOT let this delay reperfusion therapy)
- Aspirin 320 mg (4 tablets of 80 mg) chewed, then Aspirin 80 mg daily
- If Aspirin allergy : Plavix 300 mg po initial dose, then 75 mg daily
- Sublingual Nitroglycerin 0.4 mg, may be repeated at 5 minute intervals x 3. This is THE initial treatment for MI pain.
- If Chest pain not relieved, give Morphine 2mg IV every 5-10 minutes until pain relief
- Metoprolol 5 mg IV over five minutes x 3 doses (If no 2nd or 3rd degree block or Asthma or COPD)
- Oxygen 4L/ NC keep O2sat >94%
Are there absolute contraindications to Fibrinolysis?
- Significant closed head/facial trauma within 3 months
- Ischemic stroke within 3 months(within 3 hours is ok)
- Intracranial or intraspinal surgery within 2 months
- Known history of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH)
- Known structural cerebral vascular lesion
- Known malignant intracranial neoplasm
- Suspected aortic dissection
- Active bleeding or bleeding diathesis (excluding menses)
- Severe uncontrolled hypertension that is not responding to meds in ER
Relative contraindications to Fibrinolysis
- Systolic blood pressure > 180 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure > 110 mm Hg
- Prolonged CPR > 10 minutes or major surgery within 3 weeks
- History of prior ischemic stroke not within the last 3 months
- Internal bleeding within 4 weeks
- Noncompressible vascular punctures
- Dementia
- Pregnancy
- Active peptic ulcer
- Warfarin with INR >1.7
Alteplase dose:
- 15-mg IV bolus followed by
- 0.75 mg/kg (up to 50 mg) IV over 30 minutes
- 0.5 mg/kg (up to 35 mg) IV over 60 minutes.
The maximum total dose is 100 mg for patients weighing more than 67 kg.
After Alteplase patient is taken to PCI suite for angiography.
Unstable Angina / ST segment depression / T Wave Inversion or Positive Cardiac Markers:
- Monitored Bed Admission
-
Adjuvant Measures
- Intensive care monitoring for arrhythmias
- Aspirin
- Nitroglycerine 0.4mg Avoid if he has taken Viagra within 24 h or has large RV infarct
- Heparin UFH or LMWH
- GP IIb /IIIa inhibitor
- Beta Blockers : Metoprolol 25 mg po q 12h
- Monitoring
-
Early Invasive intervention of any of these high risk features are present:
- Refractory Chest Pain
- Blood pressure unstable
- Ventricular Tachycardia
- Recurrent or persistent ST deviation
-
Signs and symptoms of Heart Failure
- S3 gallop,
- pulmonary edema,
- worsening rales
- new or worsening mitral regurgitation
- High-risk findings on noninvasive stress testing
- Depressed left ventricular function (EF < 40% on noninvasive study)
Low Risk Patients (Chest Pain with Non-diagnostic EKG)
Admit
Serial Cardiac Enzymes
Repeat EKGs
RIF: Abnormalities on noninvasive imaging and physiological testing
OR
IF: High risk features appear / Dynamic EKG changes / Elevated troponin
Adjuvant therapies
Monitored bed
Consider invasive therapies
Read Other Topics
Read All Pages
Ventricular Fibrillation
It this was an unwitnessed arrest, meaning it did not happen in front of you, you should give him 5 cycles of CPR...
Read More
Infant Cpr
Perform 30 chest compressions. Use two fingers and deliver the compressions over the breastbone, just below the nipple line...
Read More